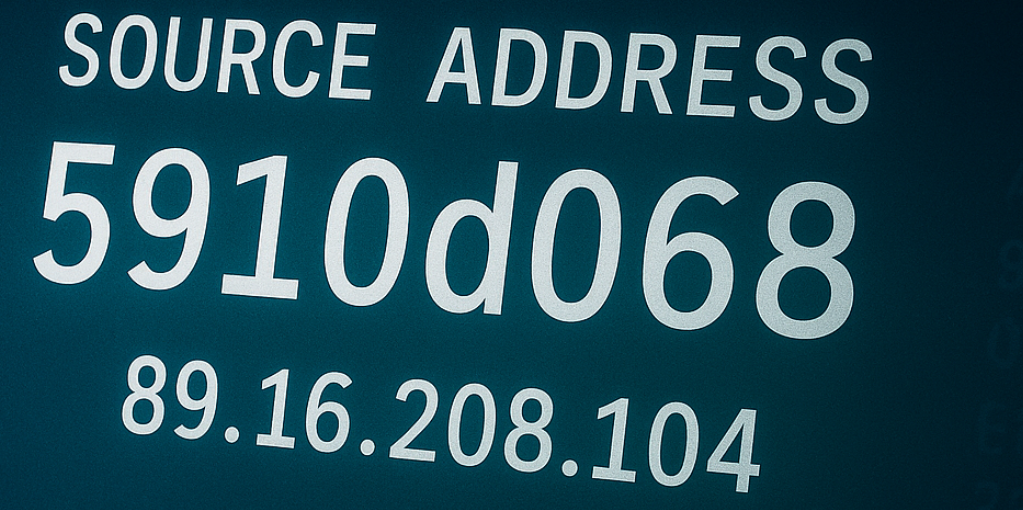Understanding Source Address 5910d068: A Comprehensive Guide to Networking and Security
In the realm of computer networking, addresses play a pivotal role in ensuring accurate data transmission between devices. One such identifier is the source address, which denotes the origin of a data packet. A specific example of this is the source address 5910d068, a hexadecimal representation that holds particular significance in networking contexts.
Decoding “5910d068”
To comprehend the essence of source address 5910d068, it’s essential to understand hexadecimal notation. Hexadecimal, or base-16, uses sixteen symbols (0-9 and A-F) to represent values. This system is often employed in computing due to its efficiency in representing binary data.
The address “5910d068” can be broken down into four pairs: 59, 10, d0, and 68. Converting each pair from hexadecimal to decimal yields:
- 59 (hex) = 89 (decimal)
- 10 (hex) = 16 (decimal)
- d0 (hex) = 208 (decimal)
- 68 (hex) = 104 (decimal)
Combining these decimal values results in the IPv4 address: 89.16.208.104. This conversion is crucial for network administrators and cybersecurity professionals when analyzing network traffic or configuring systems.
The Role of Source Addresses in Networking
In data communication, every packet transmitted over a network carries both a source and a destination address. The source address indicates where the packet originated, while the destination address specifies its intended recipient.
Understanding source addresses is vital for several reasons:
- Routing Decisions: Routers use source addresses to determine the best path for returning data to the sender.
- Access Control: Firewalls and security systems reference source addresses to permit or deny traffic based on predefined rules.
- Network Diagnostics: Tools like traceroute and ping utilize source addresses to identify the path and origin of data packets.
Source Address Selection Mechanisms
The selection of a source address can be influenced by various factors:
- Operating System Defaults: Systems often select a source address based on routing tables and interface configurations.
- Manual Configuration: Administrators can specify source addresses for particular applications or services.
- Multihomed Hosts: Devices with multiple network interfaces may choose a source address based on the destination network, ensuring optimal routing.
Security Considerations
While source addresses are fundamental for network operations, they can also be exploited:
- Spoofing: Malicious actors may forge source addresses to impersonate trusted devices, bypassing security measures.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks: Attackers can flood a network with packets bearing fake source addresses, overwhelming systems and obscuring the attack’s origin.
- Logging and Monitoring: Accurate source address information is crucial for maintaining logs, which aid in forensic analysis and compliance.
Implementing measures like ingress filtering and employing security protocols can mitigate these risks.
Source Address in Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) modifies IP address information in packet headers, allowing multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address. In this process:
- Source NAT (SNAT): Alters the source address of outgoing packets, enabling internal devices to communicate externally.
- Destination NAT (DNAT): Changes the destination address of incoming packets, directing them to the appropriate internal device.
Understanding how NAT affects source addresses is essential for configuring network services and troubleshooting connectivity issues.
Best Practices
To ensure effective use and management of source addresses:
- Regular Audits: Periodically review network configurations and logs to detect anomalies.
- Implement Access Controls: Define rules that permit or deny traffic based on source addresses.
- Educate Users: Ensure that personnel understand the importance of source addresses and the risks associated with their misuse.
Conclusion
The source address 5910d068, when decoded, reveals the IPv4 address 89.16.208.104. This example underscores the importance of understanding hexadecimal representations and their role in networking. By grasping the function and implications of source addresses, professionals can enhance network performance, bolster security, and ensure reliable communication across systems.
Recommended Articles
AWT69X Technology: Full Guide to Features, Architecture, Applications & Future
The Story of Susanne Capurso and 302 Spring Drive, East Meadow
What Answers to Pick to Get Ciel Phantomhive in Quizkie: Ultimate Guide for Anime Quiz Lovers
Orannalaura: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Meaning, Influence and Multifaceted Role in Modern Culture